SEO Web Up is one of the best SEO agencies. Their SEO strategy helped us greatly improve our search engine presence. I would definitely recommend them.
Transforming Your Online Presence with Cutting-Edge Off-Page SEO
We understand that true SEO success hinges on a comprehensive approach that extends beyond just optimizing your website. While on-page SEO focuses on refining your site’s content and structure, off-page SEO serves as the driving force behind your brand’s authority, credibility, and visibility in the digital realm.
This multifaceted strategy includes a variety of techniques designed to enhance your online reputation and connect your site with influential external signals.
In today’s competitive online environment, neglecting off-page SEO can leave your website obscured, unable to realize its full potential.
That’s why we prioritize a bespoke off-page strategy tailored specifically to your unique business goals.
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO encompasses all activities conducted outside your website that affect your rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs). This includes a wide array of strategies, such as strategic link-building, vibrant social media engagement, and impactful brand mentions—all working in concert to establish your site’s authority and relevance.
Essentially, off-page SEO shapes how your brand and website are perceived within the digital landscape. It’s not merely about having an exceptional site; it’s about being recognized as a trusted authority in your industry. The more credible and relevant your site appears to search engines, the greater your chances of achieving top rankings.
Our dedicated team is committed to implementing powerful off-page strategies that will significantly elevate your online reputation.
Why Off-Page SEO Matters
Search engines like Google utilize a sophisticated array of signals to evaluate your website’s authority and relevance to specific search queries. Strong off-page SEO is vital for positioning your site as a credible resource, directly influencing how search engines assess your legitimacy.
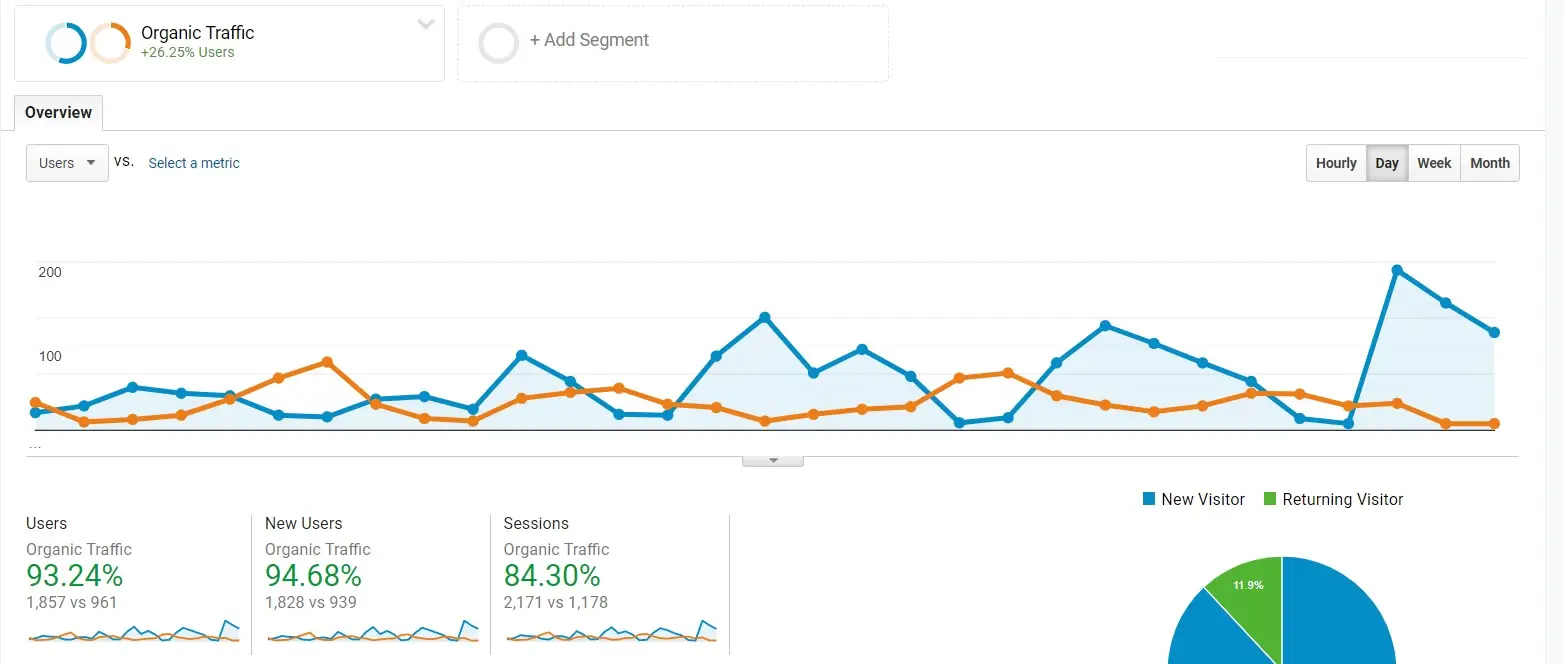
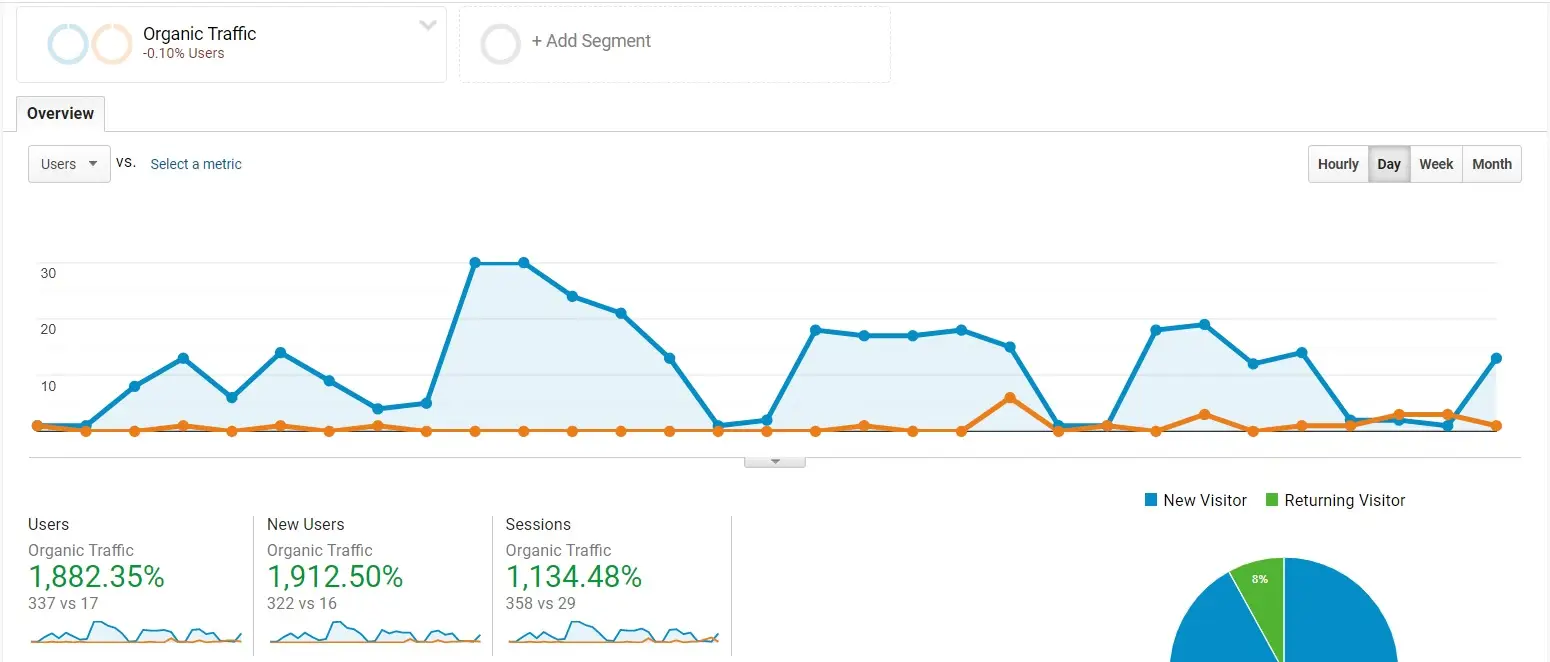
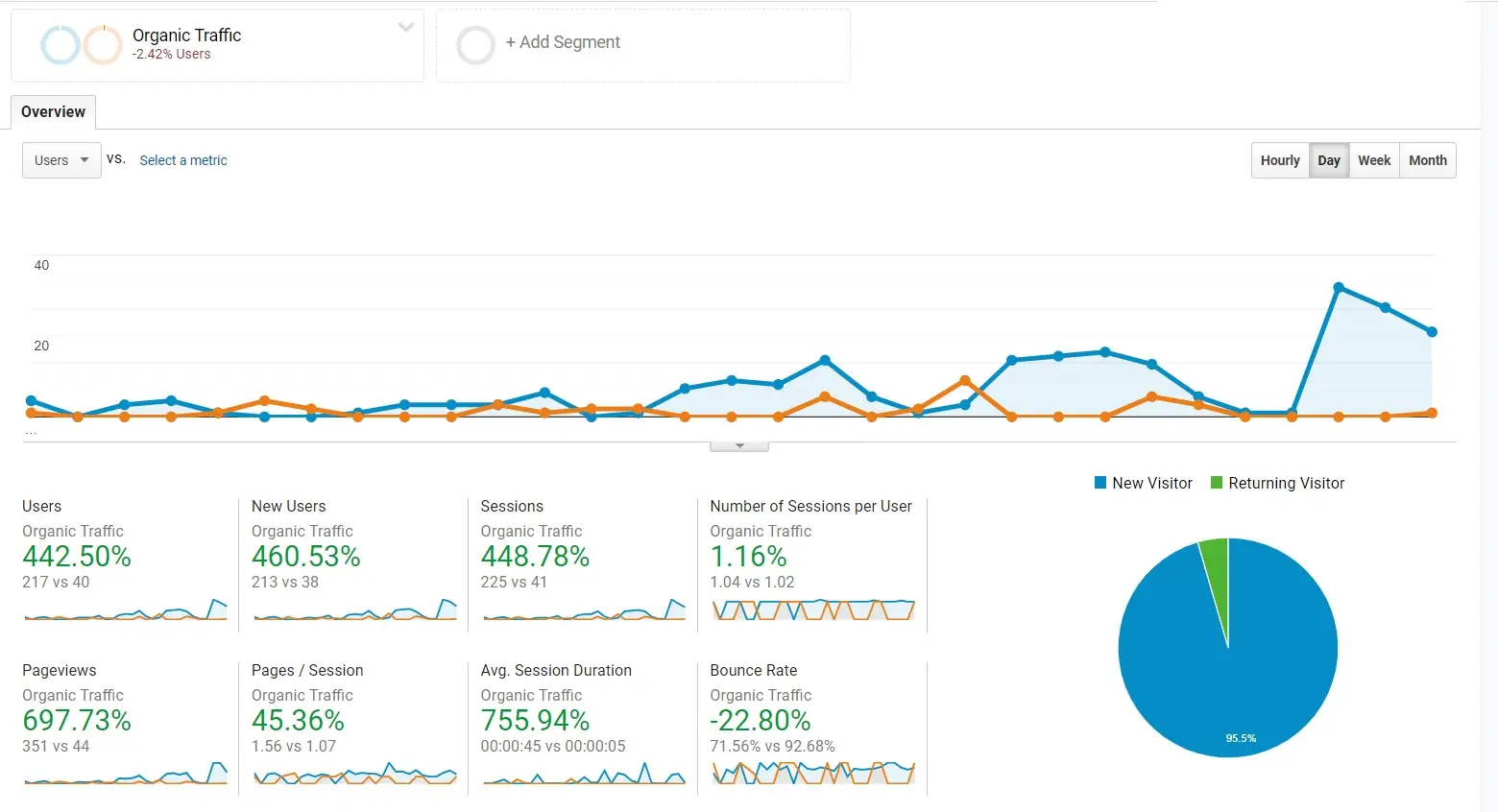
High-quality backlinks from reputable websites act as powerful endorsements, signaling to search engines that your content is both valuable and trustworthy. By enhancing your backlink profile, you not only strengthen your site’s authority but also boost your chances of climbing to the top of search results.
At SEO Web Up, we specialize in developing customized off-page SEO strategies that empower your brand to stand out in a crowded digital marketplace, ensuring you attract the attention and engagement you deserve.
We use various websites to create quality links, these include (in alphabetical order):
- Article Marketing websites
- Blogging and comments
- Directories
- eBooks, pdf and document sharing websites
- Forums
- Guest Posts
- Image sharing websites
- Infographic sharing websites
- Podcast sharing websites
- Press Release websites
- Company profile websites such as Google My Business etc.
- Question & Answer Sites
- Review websites
- Slideshow & Presentation sharing websites
- Social bookmarking
- Social Media websites
- Video sharing websites
Excellent, we are very impressed with the SEO results. Highly recommended.
SEO Web Up has highly skilled and professional SEO consultants. I strongly recommend them. Thank you.
Punye is one of the best SEO Consultants I have known. He and his team have helped us grow our business and we are seeing over 200% more leads coming in every month.
SEO Web Up is the 4th SEO company to work on our website’s SEO and I found the best, especially for our UAE branch. I am very happy with the SEO results. I truly found value for money.
Excellent efforts by Punye and his team, keep up the good work.
I'm highly satisfied with the work that SEO Web Up did for us at a reasonable cost. They're experts at SEO and very professional. Highly recommend them!
Putting our client’s success first
What is PageRank?
PageRank was the first core Google Search algorithm which is named after Larry Page (co-founder of Google). PageRank aims at estimating the importance of a webpage on the basis of number and quality of links it receives. In short it is a link analysis algorithm.
PageRank was developed as part of a research project in 1996 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin while they were studying in Stanford University. Rajeev Motwani and Terry Winograd were co-authors of the first paper about the PageRank project.
It might come as a surprise to many people that the PageRank US patent was actually assigned to Stanford University, who gave its exclusive license rights to Google in exchange for 1.8 million Google shares, which it later sold for US$336 million in the year 2005.
Original definition of PageRank
PageRank as defined in the original paper “The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine” by Sergey Brin and Lawrence Page (also co-founders of Google) is as follows:
We assume page A has pages T1…Tn which point to it (i.e., are citations). The parameter d is a damping factor which can be set between 0 and 1. We usually set d to 0.85. There are more details about d in the next section. Also C(A) is defined as the number of links going out of page A. The PageRank of a page A is given as follows:
PR(A) = (1-d) + d (PR(T1)/C(T1) + … + PR(Tn)/C(Tn))
Note that the PageRanks form a probability distribution over web pages, so the sum of all web pages’ PageRanks will be one.
PageRank or PR(A) can be calculated using a simple iterative algorithm, and corresponds to the principal eigenvector of the normalized link matrix of the web.
What are Link Schemes?
Google doesn’t provide any clear definition of link schemes. It only says that any links (which includes links from other sites as well as external links) intended to manipulate PageRank or a site’s ranking in Google search results may be considered part of a link scheme by Google. However Google Webmaster Guidelines specifically informs webmasters to avoid participating in link schemes.
Examples of link schemes include:
- Buying or selling links that pass PageRank.
- Excessive link exchanges
- Large-scale article marketing or guest posting campaigns with keyword-rich anchor text links
- Text advertisements that pass PageRank
- Advertorials or native advertising where payment is received for articles that include links that pass PageRank
- Links with optimized anchor text in press releases distributed across other sites
- Low-quality directory or bookmark site links
- Keyword-rich, hidden or low-quality links embedded in widgets that are distributed across various sites
- Widely distributed links in the footers or templates of various sites
- Forum comments with optimized links in the post or signature
What was Penguin Algorithm update?
Penguin was a core algorithm update by Google that negatively affects websites practicing aggressive webspam or SEO tactics, including websites that use low quality link building techniques as well as keyword stuffing in order to rank higher in search results.
The main thing to remember is that Penguin primarily looks at the source website or webpage and not the target website. Source website is the website from which the backlink is sourced whereas the target website is the website which is linked from such link.
Another main point to keep in mind is that Google tends to devalue such links and not necessarily penalize the target website.
Penguin looks at various aspects of the source webpage, including the quality and relevance of the content on the page from which the link is sourced.
Penguin update history:
From wayback in 2012 when Penguin was first rolled out till 2016 when Penguin became part of Google’s core algorithm, it is essential to understand that it went through various stages and take note of the publically announced dates when major updates happened:
- April 24, 2012 – Penguin 1.0 rolls out
- May 25-26, 2012 – Next stage of Penguin 1.0 initial update
- October 5, 2012 – A Penguin data update
- May 22, 2013 – Penguin 2.0 rolls out
- October 4, 2013 – A Penguin data update
- October 17, 2014 – Penguin 3.0 rolls out
- September 23, 2016 – Penguin 4.0, Penguin becomes part of Google’s core algorithm. Google announces on its Webmaster Central Blog that after rigorous development and testing, Penguin’s data will now get refreshed in real time and it won’t be commenting on future refreshes to its Penguin algorithm update. This meant that changes will be visible much faster, typically taking effect shortly after Google recrawls and reindexes a page. Google also explained some more features of this update such as that Penguin will now get more granular, which translates to that Penguin will now devalue spam by adjusting ranking based on spam signals, rather than affecting ranking of the whole site.